Metal furniture manufacturing has undergone a revolutionary transformation with the introduction of advanced automation technologies. Among the most significant innovations is the implementation of sophisticated bending equipment that delivers unprecedented precision and consistency in metalworking operations. Modern manufacturing facilities are increasingly adopting automated solutions to meet the growing demand for complex geometries and tight tolerances in furniture components. The evolution from traditional manual bending methods to computer-controlled systems has enabled manufacturers to achieve levels of accuracy that were previously unattainable, while simultaneously reducing production time and material waste.
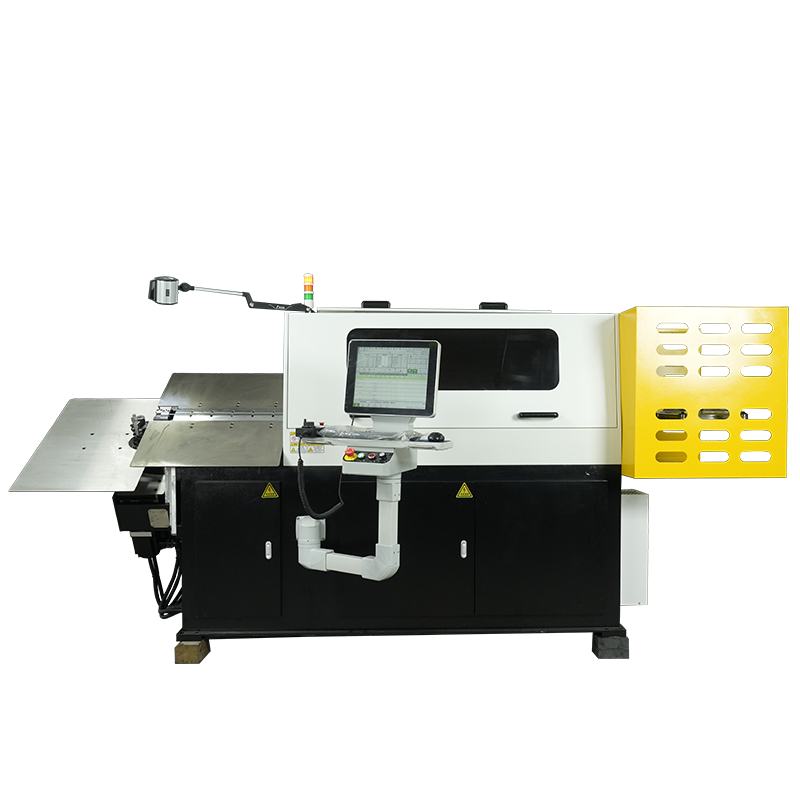

Understanding Advanced Metal Bending Technology
Core Principles of Automated Bending Systems
Automated bending systems operate on sophisticated mathematical algorithms that calculate precise bend angles, radii, and material springback compensation. These systems utilize servo-driven actuators and high-resolution encoders to position bending tools with micron-level accuracy. The integration of real-time feedback sensors enables continuous monitoring of force application and material deformation throughout the bending process. This technological foundation ensures that each bend meets exact specifications while maintaining consistent quality across entire production runs.
The computer numerical control (CNC) architecture forms the backbone of modern bending operations, allowing operators to program complex sequences of bends with multiple angles and orientations. Advanced software interfaces provide intuitive programming capabilities, enabling rapid setup changes and optimization of bending parameters. The system's ability to store and recall thousands of program configurations streamlines production workflows and reduces setup time between different furniture components.
Material Handling and Positioning Accuracy
Precision material handling systems work in conjunction with bending mechanisms to ensure accurate positioning of workpieces throughout the manufacturing process. Automated clamping systems secure materials with consistent pressure distribution, preventing slippage or deformation during bending operations. Multi-axis positioning tables enable complex three-dimensional orientations, allowing for the creation of intricate furniture geometries that would be impossible to achieve through conventional methods.
The integration of vision systems and laser measurement devices provides real-time verification of material positioning and dimensional accuracy. These quality control measures detect deviations from specified tolerances before bending operations commence, preventing the production of defective components. The automated rejection system removes non-conforming parts from the production line, maintaining consistent quality standards throughout the manufacturing process.
Precision Enhancement Mechanisms
Springback Compensation Technology
One of the most critical challenges in metal bending is the phenomenon of springback, where materials partially return to their original shape after bending forces are removed. Advanced bending systems incorporate sophisticated springback compensation algorithms that predict and counteract this behavior based on material properties, thickness, and bend geometry. These predictive models utilize extensive databases of material characteristics and historical bending data to calculate precise overbend angles that result in final parts meeting exact specifications.
The compensation system continuously learns and adapts through machine learning algorithms that analyze the relationship between predicted and actual bend results. This self-improving capability ensures that precision increases over time as the system accumulates more data about specific materials and bending scenarios. The result is a dramatic reduction in trial-and-error setup procedures and improved first-part accuracy in production environments.
Force Control and Monitoring Systems
Precision force control represents another crucial advancement in modern bending technology. Load cells and pressure sensors provide real-time feedback about the forces applied during bending operations, enabling the system to maintain consistent bending conditions regardless of material variations or tool wear. This force monitoring capability prevents over-stressing of materials while ensuring complete formation of bend radii according to design specifications.
The force control system also serves as a quality assurance mechanism by detecting anomalies that might indicate material defects, tool problems, or setup errors. Automatic adjustment of bending parameters based on force feedback maintains optimal bending conditions throughout production runs. This adaptive capability significantly reduces the occurrence of defective parts and minimizes material waste in furniture manufacturing operations.
Impact on Manufacturing Efficiency
Production Speed and Throughput Optimization
Modern bending equipment dramatically increases production throughput while maintaining precision standards that exceed traditional manufacturing methods. Automated systems can complete complex bending sequences in seconds rather than minutes, enabling manufacturers to meet tight delivery schedules and respond quickly to market demands. The elimination of manual setup and adjustment procedures reduces cycle times and allows for continuous production operations with minimal operator intervention.
The implementation of a 3D Bending Machine with high-output capabilities transforms production economics by enabling manufacturers to produce complex furniture components at volumes previously achievable only with simple geometries. Batch processing capabilities allow simultaneous bending of multiple parts, further multiplying throughput advantages. The consistent quality output eliminates downstream inspection and rework operations that traditionally consume significant production time.
Quality Consistency and Repeatability
The automated nature of advanced bending systems ensures absolute repeatability across production runs, eliminating the variability inherent in manual operations. Each part produced meets identical specifications regardless of operator skill level or fatigue factors that might affect manual bending quality. This consistency enables furniture manufacturers to guarantee precise fit and finish across entire product lines, enhancing brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
Statistical process control capabilities built into modern bending systems provide comprehensive quality documentation and traceability throughout the manufacturing process. Real-time quality monitoring generates detailed reports that facilitate continuous improvement initiatives and regulatory compliance requirements. The elimination of human error factors results in dramatically reduced scrap rates and improved material utilization efficiency.
Applications in Furniture Manufacturing
Chair Frame Production
Chair frame manufacturing represents one of the most demanding applications for precision bending technology due to the complex three-dimensional geometries required for ergonomic design and structural integrity. Advanced bending systems excel at creating the precise curves and angles necessary for comfortable seating while maintaining the structural strength required for safety certifications. The ability to program multiple bend sequences enables production of chair frames with varying sizes and configurations without extensive tooling changes.
The precision achieved through automated bending ensures perfect alignment of mounting points and connection interfaces, facilitating seamless assembly operations downstream. Consistent bend radii eliminate stress concentrations that could compromise structural integrity over time. The repeatability of automated systems enables manufacturers to produce matched sets of chair frames with identical characteristics, essential for commercial furniture applications where uniformity is critical.
Table Base and Support Structure Manufacturing
Table base production benefits significantly from the precision capabilities of modern bending equipment, particularly in creating the complex support structures required for large conference tables and specialized work surfaces. The ability to maintain precise angles and dimensional accuracy ensures proper load distribution and structural stability across varying table sizes and configurations. Automated bending eliminates the dimensional variations that can cause wobbling or instability in finished table assemblies.
The versatility of programmable bending systems allows manufacturers to produce table bases with varying heights, widths, and support configurations using standardized tooling setups. This flexibility enables rapid response to custom orders while maintaining cost-effective production methods. The precision achieved in base component manufacturing facilitates simplified assembly procedures and reduces the need for adjustment operations during final assembly.
Economic Benefits and ROI
Labor Cost Reduction and Skill Requirements
The implementation of automated bending systems significantly reduces labor requirements while upgrading the skill level of remaining operators from manual labor to technical supervision roles. Operators transition from performing repetitive physical tasks to monitoring multiple automated stations and managing production schedules. This evolution improves job satisfaction while enabling manufacturers to attract and retain higher-skilled personnel who contribute more value to operations.
The reduction in manual handling requirements eliminates ergonomic concerns associated with traditional bending operations, reducing workers' compensation costs and improving workplace safety metrics. Automated systems also eliminate the lengthy training periods required to develop manual bending skills, enabling rapid scaling of production capacity during peak demand periods. The consistent output quality reduces the need for specialized quality control personnel and minimizes rework operations that consume additional labor resources.
Material Utilization and Waste Reduction
Precision bending technology dramatically improves material utilization rates through accurate calculation of bend allowances and elimination of trial-and-error setup procedures. Advanced nesting algorithms optimize material layouts to minimize waste while ensuring proper grain orientation for optimal bend quality. The ability to achieve correct dimensions on the first attempt eliminates the material waste associated with prototype development and setup optimization.
The consistent quality output from automated systems reduces downstream rejection rates, minimizing the material costs associated with defective parts. Real-time quality monitoring prevents the production of entire batches with systematic errors, avoiding the significant material losses that can occur with manual operations. The improved material utilization directly impacts profitability while supporting sustainability initiatives through reduced resource consumption.
FAQ
What level of accuracy can modern bending machines achieve in furniture manufacturing
Modern automated bending systems routinely achieve accuracy levels within ±0.1 degrees for bend angles and ±0.5mm for dimensional tolerances. This precision level far exceeds the capabilities of manual bending methods and meets the stringent requirements of high-end furniture applications. The combination of servo-driven positioning systems, real-time feedback control, and advanced compensation algorithms enables consistent achievement of these accuracy standards across extended production runs.
How do these machines handle different types of metals used in furniture production
Advanced bending systems incorporate extensive material databases containing the properties of various metals commonly used in furniture manufacturing, including aluminum, steel, stainless steel, and specialty alloys. The system automatically adjusts bending parameters based on material selection, accounting for differences in elastic modulus, yield strength, and springback characteristics. This adaptive capability ensures optimal results regardless of material type while minimizing setup time and trial runs.
What maintenance requirements are associated with precision bending equipment
Maintenance requirements for modern bending systems focus primarily on preventive care rather than reactive repairs. Regular calibration of positioning systems, lubrication of mechanical components, and inspection of tooling wear patterns maintain optimal performance levels. Most systems incorporate predictive maintenance capabilities that monitor component condition and provide advance warning of potential issues, enabling scheduled maintenance that minimizes production disruption.
Can these systems be integrated with existing furniture manufacturing workflows
Modern bending systems are designed with integration capabilities that enable seamless incorporation into existing manufacturing workflows. Standard communication protocols facilitate connection with enterprise resource planning systems, quality management databases, and downstream assembly operations. The modular design of these systems allows for phased implementation that minimizes disruption to ongoing production while enabling gradual optimization of overall manufacturing efficiency.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Advanced Metal Bending Technology
- Precision Enhancement Mechanisms
- Impact on Manufacturing Efficiency
- Applications in Furniture Manufacturing
- Economic Benefits and ROI
-
FAQ
- What level of accuracy can modern bending machines achieve in furniture manufacturing
- How do these machines handle different types of metals used in furniture production
- What maintenance requirements are associated with precision bending equipment
- Can these systems be integrated with existing furniture manufacturing workflows